The Role of Hearing Tests in Preventative Health Care
Most of us are used to scheduling annual checkups for our vision, dental

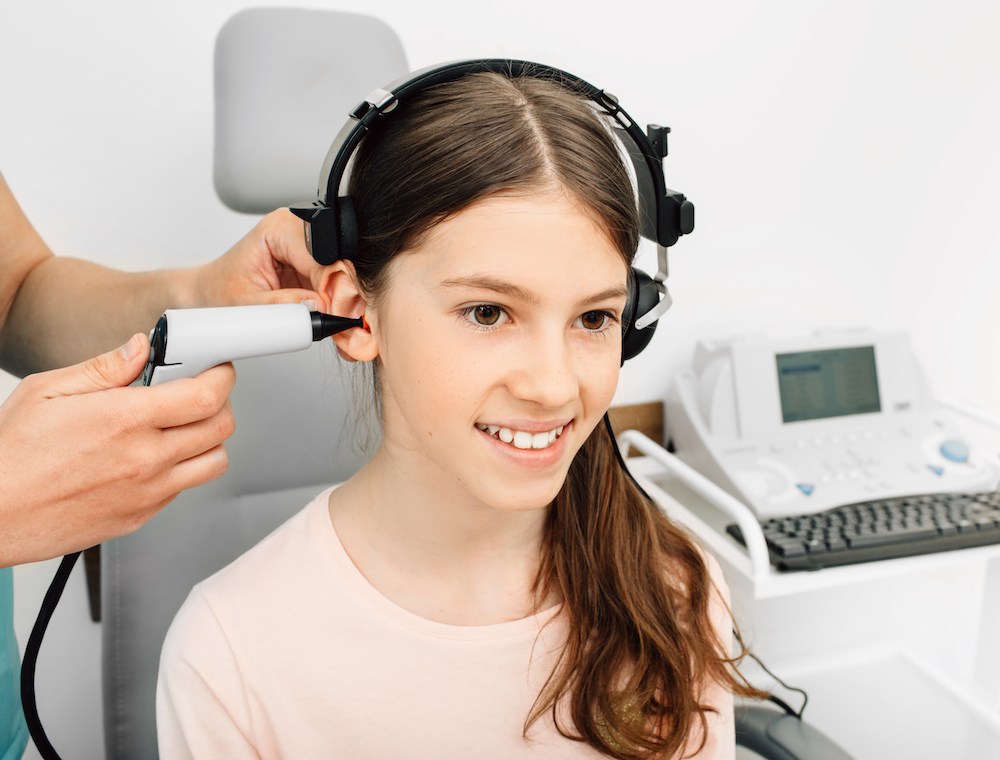
Most of us are used to scheduling annual checkups for our vision, dental
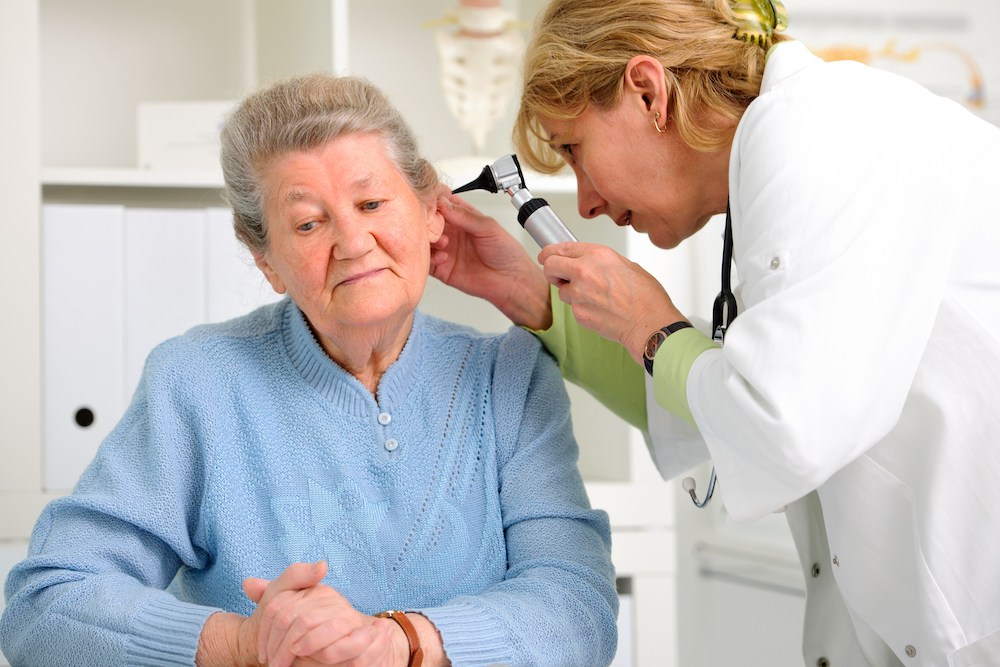
Summer tends to be louder than the rest of the year. You’re probably
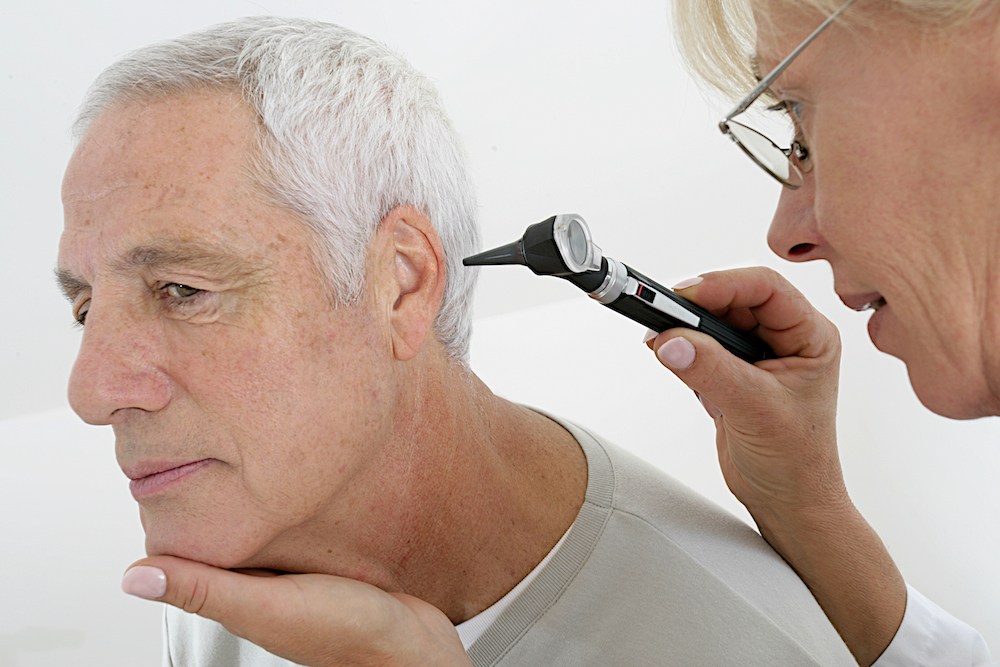
Hearing testing has come a long way from the basic beep tests many people